5g millimeter wave has many outstanding advantages, such as large frequency broadband capacity, easy combination with beamforming and ultra-low delay, which is conducive to promoting the development of industrial Internet, AR / VR, cloud games, real-time computing and other industries. At the same time, millimeter wave can support the deployment of dense areas, carry out high-precision positioning and high equipment integration, which will help to promote the miniaturization of base stations and terminals.
As the world begins to get out of the shadow of COVID-19, the continuous improvement of 5G penetration is becoming an important driving force for global economic growth. According to the prediction of GSMA, from 2021 to 2025, the capital expenditure of global mobile operators will reach US $900 billion, of which 80% will be used for 5g business; By the end of 2025, the number of 5g mobile connections will account for one fifth of the global total, close to 2 billion. China will continue to lead the world, with the largest number of users in the world (more than 830 million), and the total number of 5g connections will also exceed 800 million. 90% of the capital expenditure of operators of US $210 billion will be used for 5g.
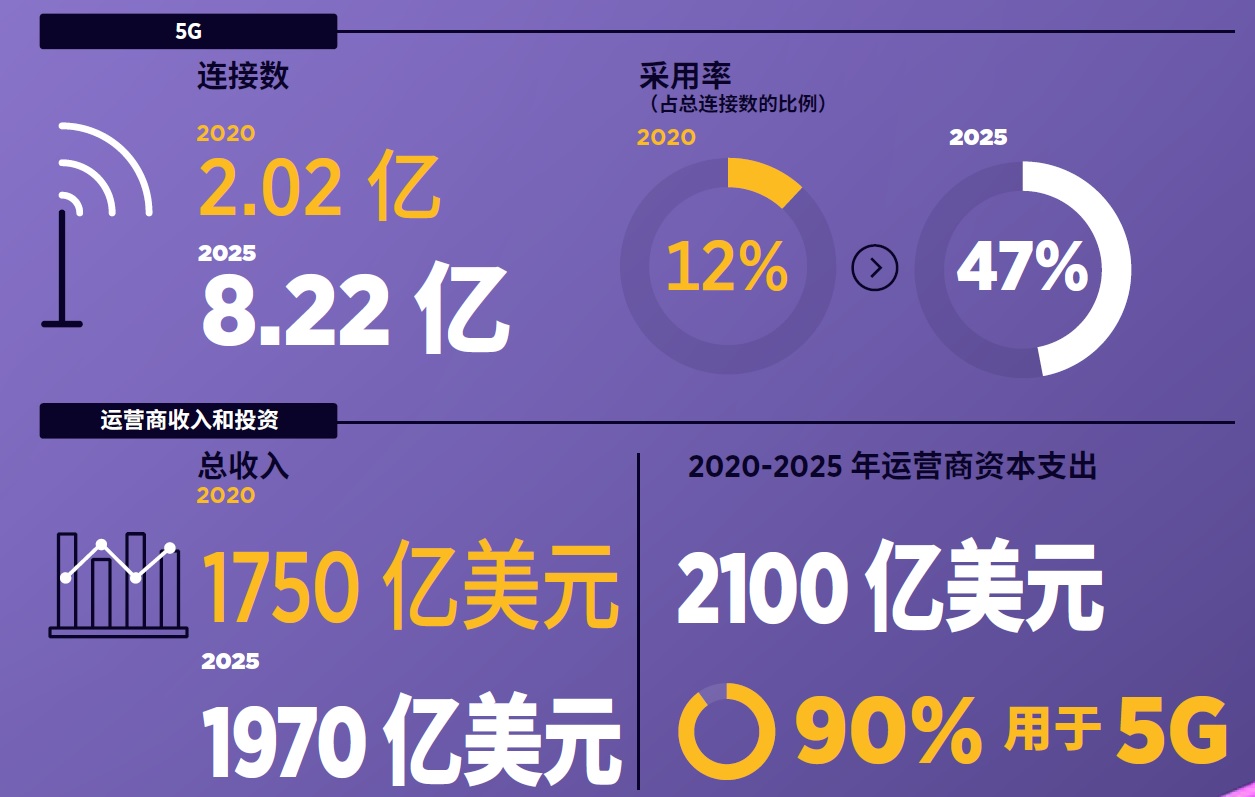
China's 5g mobile economy (source: GSMA)
Si Han, President of GSMA Greater China, pointed out in his speech at the second 5g millimeter wave industry summit forum that the distribution of millimeter wave spectrum is an important node on the road of 5g development. For the Asia Pacific region and the global market, 5g, as a new economic growth point, will further promote the development of digital economy. It is expected that the Chinese government and industry will further promote the millimeter wave spectrum planning and layout in advance as soon as possible.
5g millimeter wave has many outstanding advantages, such as large frequency broadband capacity, easy combination with beamforming and ultra-low delay, which is conducive to promoting the development of industrial Internet, AR / VR, cloud games, real-time computing and other industries. At the same time, millimeter wave can support the deployment of dense areas, carry out high-precision positioning and high equipment integration, which will help to promote the miniaturization of base stations and terminals. She said that driven by the 5g application 'sailing' action plan (2021-2023), China will soon usher in a hundred flowers bloom and large-scale mature development of 5g applications in consumers and industries.
According to the latest data from the Ministry of industry and information technology, as of August this year, China has built a total of 1.037 million 5g base stations, accounting for more than 70% of the world; 5g end users exceeded 400 million, making it the largest user group in the world; From January to August this year, the domestic shipment of 5g mobile phones reached 168 million, a year-on-year increase of 80%; There are more than 10000 5g application cases, '5g + industrial Internet' has become one of the most active fields of application innovation, covering 22 important industries such as electronic equipment manufacturing, steel, electric power and mining.
'If the first half of 5g is a table tennis game that reflects the single player technology of telecom operators, then in the second half, 5g will face expanding application demand, and 5g will become a football game with different roles and participation with vertical industries.' Wen Ku, vice president and Secretary General of China Communications Standardization Association, said that although China has played a good table tennis game, it is difficult to play football, It is hoped that the industrial chain will cooperate to play both table tennis and football well. At the same time, 'only by doing 5g well can we do 6G well'. The development of millimeter wave needs to strengthen industry university research cooperation, jointly promote the maturity of millimeter wave industry, and accumulate experience for the possible use of 6G terahertz in the future.
What kind of 5g network does the industry need
According to the economic analysis of 5g millimeter wave released by GSMA in 2021, through the comprehensive analysis of the development cost, gain and economic benefits of 5g millimeter wave, it shows that the combination of 5g millimeter wave and if C-band will bring obvious cost optimization and gain to operators in the scenario of high-density urban deployment and fixed wireless access.
According to bi Qi, chief expert of China Telecom, director of the expert committee of the Telecommunications Research Institute and academician of Bell Laboratories, up to now, there are more than 4500 5g vertical industry applications in China, more than 50% of which are applied in industry, 20% in government services, 10% in transportation and medical industries, and the rest are applied in education, finance and other fields respectively.
'Now, in order to do a good job in the application of vertical industry, we must pay attention to two challenges: one is how to solve the fragmentation of vertical industry and make the wireless communication industry chain develop rapidly in the vertical industry; the other is how to better reduce the price of 5g terminals and modules.' bich said that in the future, China Telecom and China Unicom will be based on 3.5GHz TDD and 2.0GHz FDD networks, Continue to deploy 5g millimeter wave network to meet the needs of various industries.
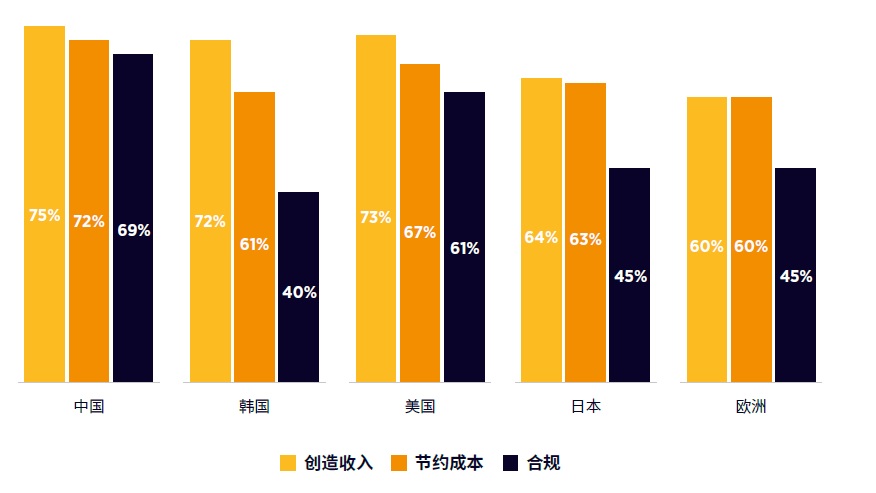
Revenue generation and cost saving are still the primary criteria to test the success of the Internet of things; However, for Chinese enterprises, compliance has become equally important after the epidemic (source: GSMA)
Ma Hongbing, general manager of science and technology innovation Department of China Unicom, put forward the view that millimeter wave will help operators 'have more legs and more ways' in networking. He said that millimeter wave has greater advantages in accurate positioning than other bands, and can achieve centimeter level or even higher precision positioning, which makes the prospect of millimeter wave in VR and other applications widely promising.
However, he also reminded the industry that 5g is a combined technology. Although it has the characteristics of large bandwidth, low delay, high speed and high reliability, it still needs edge cloud or UPF sinking to meet the network demand. This means that 5g is not only facing the improvement of base station and bandwidth, but also needs to adjust and cooperate in the network architecture in order to really support thousands of lines and industries.
At the same time, the launch of the 'sailing' action plan of the Ministry of industry and information technology also shows that 5g and industry applications are now moving from the 'ice breaking' stage to 'deep blue', which is very difficult. Operators' own understanding of the industry is not deep enough. 5g network and vertical industries must form a close consortium before they can continue to move towards deep water.
Of course, like beech, Ma Hongbing also pointed out that it is particularly important to reduce the cost of millimeter wave as soon as possible in order to carry out large-scale promotion.
Ding Haiyu, director of wireless and terminal Technology Research Institute of China Mobile Research Institute, said that China Mobile has built 700000 5g base stations, and has launched an industry-specific network product system of 'preferential, exclusive and exclusive' for 18 key industries such as mines, ports, medical treatment and factories since 2020. However, in his opinion, the network performance is not mature enough, the cost is not low enough, the network industry collaboration is not deep enough, and the end-to-end standardization is not fast enough, which are the four most urgent challenges for the application of 5g industry. Millimeter wave has excellent performance improvement in terms of high reliability, high performance and low delay, which can accelerate the high-quality development of the industry.
'When 5g is applied to the automotive industry, we need to pay attention to three major issues: cost, technology maturity and scale deployment of 5g network. Whether operators can provide stable, efficient and secure 5g network determines the deep integration between the automotive industry and 5g.' Zhang Zhiqiang, senior manager of IT infrastructure department / Information Security Department of BAIC Foton automotive, shared his views in combination with the characteristics of the automotive industry.
Lu Qingjun, representative of the medical industry, director of the office of the national telemedicine and Internet Medical Center and director of the Development Office of the China Japan Friendship Hospital, pointed out that the demand of '5g + medical' for the network emphasizes certainty and security on the basis of high throughput and low delay, which can also be said to be the comprehensive attributes of 5g (certainty, mobility, security, real-time, rapidity and specificity) And so on. It also includes the urgent demand for MEC and AI capabilities. MEC plays an irreplaceable role in supporting medical AI. However, at present, the maturity of AI system is insufficient, MEC resources have not sunk into medical institutions, and there is still a long way to go for clinical application.
'Medical treatment is one of the most complex industries. We had in-depth discussions with China Mobile and China Telecom on how to establish a private medical network and made a lot of plans, but none of them satisfied us.' Lu Qingjun said that they had made a rough statistics. Considering multiple factors such as safety, performance and cost, At present, no more than 800 of the more than 23 hospitals above grade II have opened 5g, accounting for less than one third. Even if it is opened for use, it is only some local small scene applications. It is difficult to see some rigid and irreplaceable needs under the background that both doctors and patients are not opened.
'Many hospitals in the grassroots and remote areas are not very clear about what 5G is, and many doctors do not have 5G mobile phone. This brings great inconvenience to work coordination.' he stressed that the medical profession is characterized by 'no mistakes', and that hospitals prefer 'mature' network systems to advanced technologies. Therefore, in the recently concluded medical special research, through the joint efforts with operators, telecom equipment manufacturers and scientific research institutions, 12 mature applications such as exhibition, remote diagnosis and mobile ward round have been included.
However, it is noteworthy that 'remote operation' is excluded. Lu Qingjun explained that although several hospitals had achieved a 5g delay of only 5 milliseconds, which was a beautiful figure, it was the result of heavy support at a great cost, and the cost was not replicable; Secondly, the 256 millisecond delay it really brings comes from the terminal, which is unacceptable to the doctor because he is completely unable to control in this process; Third, the cost is still high, so it is difficult to go deep into the clinical application of grass-roots hospitals.
'What urgently needs to be solved now is the breakthrough of 5g applications from 'one to n', and the core reason for choosing 12 categories of application scenarios is that these applications can be rapidly popularized, and large-scale effects will soon occur in large-scale use in the future,' Lu Qingjun said.
How does millimeter wave continue to accumulate force forward?
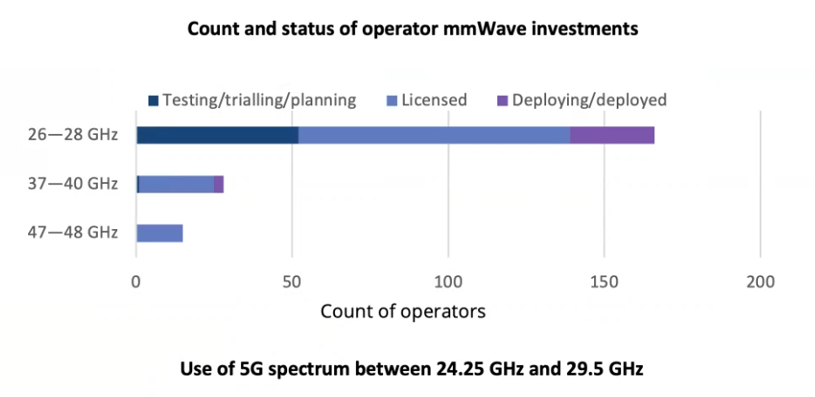
According to the data shared by Joe Barett, President of GSA, 186 operators in 48 countries are planning to develop 5g on the 26-28ghz, 37-40ghz and 47-48ghz millimeter wave spectrum. 134 operators in 23 countries hold licenses and can carry out millimeter wave deployment. North America, Europe and Asia account for 75% of all spectrum deployment. Among them, 26-28ghz is the millimeter wave band most deployed and licensed, followed by 37-40ghz, and UHF frequencies above 48ghz are still the focus of the industry.
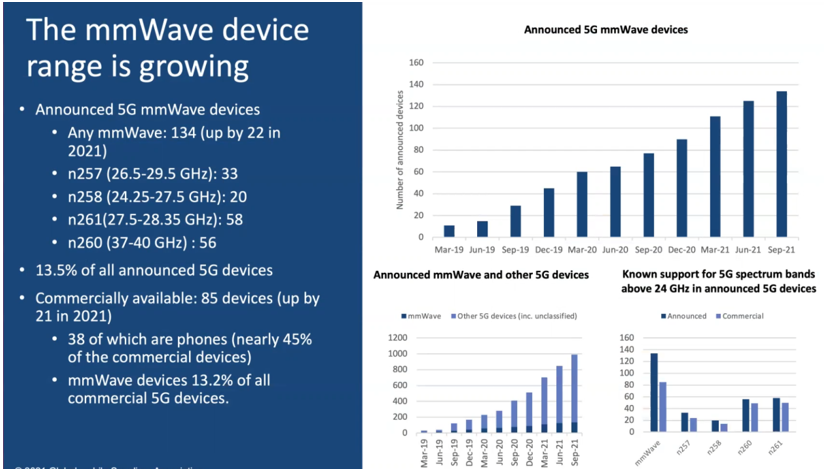
In terms of millimeter wave equipment, as shown in the figure below, there are 134 kinds of millimeter wave equipment, an increase of 22 over the beginning of 2021. Among the four key frequency bands of n257, n258, n260 and n261, manufacturers have released 33 / 20 / 56 / 58 kinds of millimeter wave equipment respectively, accounting for 13.5% of the total number of 5g equipment released. In terms of commercial 5g millimeter wave, 85 kinds of equipment have been put into commercial use, an increase of 21 over the beginning of 2021, of which 38 are mobile phones, accounting for 45% of all commercial equipment.
As we all know, millimeter wave and sub-6ghz band are important technologies for 5g. According to Xu Ying, R & D director of Qualcomm China, many traditionally regarded as mobility challenges faced by millimeter wave, such as limited coverage and high cost, only supporting line of sight transmission, only for fixed use cases, immature RFIC Technology, etc, Through more than 20 years of continuous R & D and innovation, it has been very well solved.
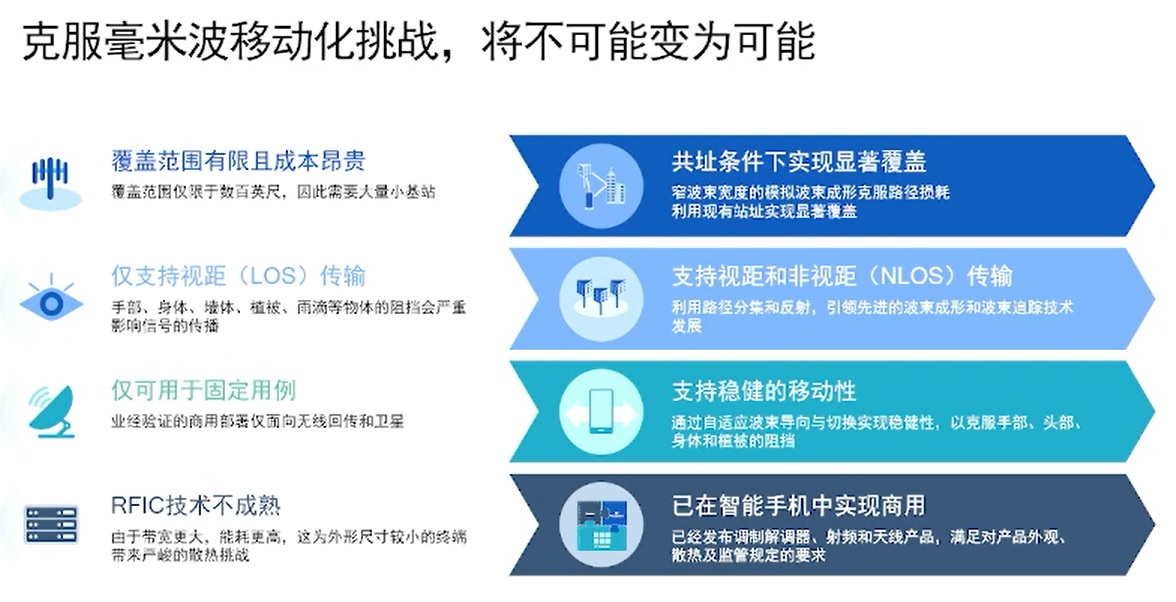
Mobile challenges faced by 5g millimeter wave (image source: Qualcomm)
For millimeter wave application scenarios, Xu stressed that not all application scenarios need millimeter wave coverage. The most important application scenarios can be summarized in four words: hot spot coverage, including enterprise indoor deployment, indoor / outdoor venues, transportation hubs, fixed wireless access, industrial Internet of things and other fields.

The most important application scenario of 5g millimeter wave is hot spot coverage (image source: Qualcomm)
'I often tell my colleagues that China is very suitable for millimeter wave applications because China has a large population density, and densely populated places such as airports, subway stations and stadiums are very suitable for millimeter wave applications.' taking the 2021 American football season finals as an example, Xu introduced Qualcomm's support for operators to conduct millimeter wave commercial tests in large stadiums and gymnasiums. The data shows that the total traffic supported by 5g millimeter wave is 4.5tb, and the peak download speed in some scenes reaches 3gbps, which is 20 times the peak download speed of 4G LTE, and it is also the peak capacity and rate that can not be realized by sub-6ghz.
The 5g millimeter wave standard is still evolving. Integrated access and return (IAB), enhanced beam management, power saving characteristics, dual connection optimization, positioning and other functions are added to the completed R16 project. In R17 and future version projects, IAB support for distributed deployment, optimized network coverage and beam management, expanded spectrum support, new use cases other than embB Positioning and enhancement will become the focus.
However, although 5g millimeter wave has many advantages and many challenges on the way forward have been solved, Yang Ning, Minister of oppo standards research department, still pointed out that from the actual situation of China, the allocation of 5g millimeter wave basic resources, such as which frequency band can be tested? What frequency bands can operators deploy? It is still not clear enough, so the effect of promoting the industry is not significant.
Second, the typical disadvantage of millimeter wave is that the coverage is relatively limited. How to ensure the connection between network and terminal and overcome the disadvantage of limited coverage is a problem to be solved. At the same time, considering that millimeter wave has the advantages of large bandwidth and multiple antennas, but it will bring challenges to the terminal, especially the heating and power consumption of the terminal, how to avoid the challenges caused by heating and power consumption from the perspective of technology is also an issue to be considered in the industrial development.
Third, for the overall deployment of 5g millimeter wave, whether on the network side or terminal side, the cost of devices and chips is still higher than that of sub-6ghz. How to reduce the cost of networks and terminals is also a challenge for the industry.
Liu Qi, director of radio resources research department of Radio Research Center of China Academy of information and communication, supplemented it from the perspective of research. He pointed out that the first is to strengthen the supply of millimeter wave technology from the supply side. In terms of standards, in addition to 3GPP's 5g millimeter wave standard, we should also promote the standardization process of 5g applications, including core chips and devices, especially those with large millimeter wave bandwidth; The second is the demand side. 'From the perspective of the industry, demand exists, but how to meet the demand of the industry through supply is the result of the joint efforts of both sides and even multiple parties. We need to jointly accelerate the standardization process to solve the problem of industry fragmentation.'